Central Limit Theorem
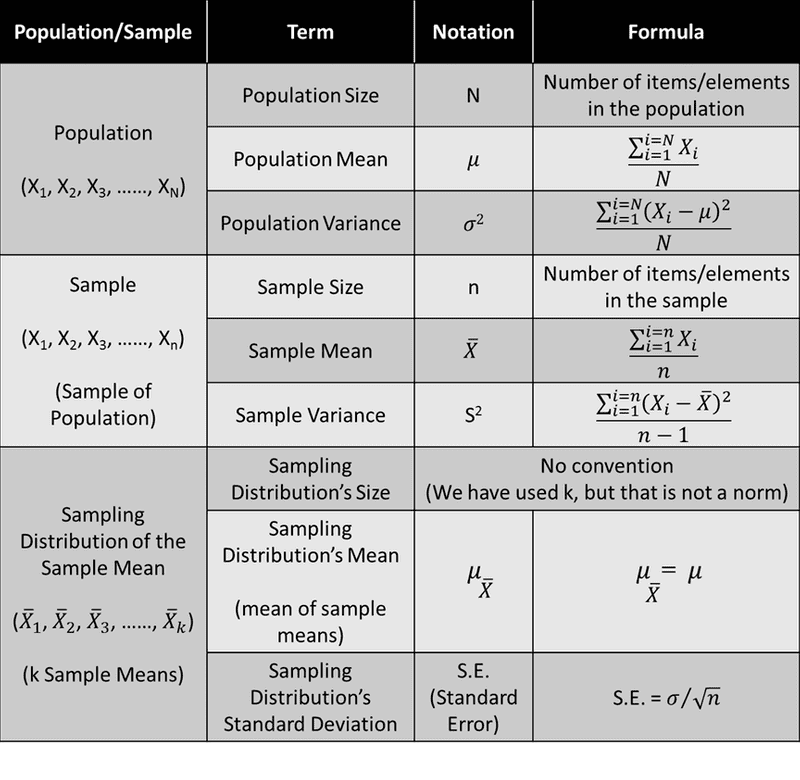
Sampling Terminology
- Sample Mean ()
- Population Mean ()
- Sample Size ()
- Population Size ()
- Population Standard Deviation ()
- Sample Standard Deviation ()
Why taking large number of samples is good?
- removes sample bias by accomodating the diversity that is inherent in the population
sampling distribution's standard deviation (standard error) =
Central Limit Theorem
- Sampling distribution's mean () = population mean ()
- sampling distribution's standard deviation (standard error) =
- for n > 30, the sampling distribution becomes normally distributed
We can use the central limit theorem to calculate population mean from sample means.
Confidence Level
- Probability associated with the claim is called confidence level
-
Z* values for commonly used confidence levels
Confidence Level Z* 90% +-1.65 95% +-1.96 99% +-2.58
Margin of Error
- Maximum error made in sample mean is called margin of error
-
Margin of error between population mean and sample mean:
- Z*: Z value
- S: standard deviation
- n: sample size
Confidence Interval
- Final interval of values is called confidence interval
- Confidence interval = (),
Takeaways
- When the population size is large, it is not feasible to collect values from each of the data points
- We can use sampling, where we take a subset of data and use it for estimating values for the whole population
- We should take large number of samples as it removes sample bias by accommodating the diversity that is inherent in the population
- Central limit theorem can be used to find population mean by sample means.
- Using Central Limit Theorem, we can assume that sample mean in normally distributed (given that sample size is greater than 30)
- We can therefore apply properties of normal distribution to answer questions such as what is the probability that the population mean will be within certain limits w.r.t to sample mean. This probability is called the confidence level.
- The interval value is called the confidence interval. It is given by the formula: [] to [] where Z* corresponds to the Z table, S is the standard deviation of the sample.
Additional Information
4 types of sampling
- random
- opportunity
- volunteer - whoever is available
- stratified - selection from subgroups